About MOLM-13
The MOLM-13 cell line is a human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell line that was initially established in 1986 by the Rolf Marschalek lab. It was derived from bone marrow samples obtained from a 62-year-old woman diagnosed with AML. Morphologically, MOLM-13 cells closely resemble myeloblasts and are typically cultured in suspension. A defining genetic characteristic of the MOLM-13 cell line is the presence of the t(9;11)(p22;q23) translocation. This translocation results in a fusion between the mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) gene and the AF9 protein. AF9 is a subunit of the MLLT3 super elongation complex, which plays a vital role in transcriptional regulation. Dysfunction of this subunit affects various crucial pathways, including positive transcription regulation, canonical Wnt signaling, and hematopoietic stem cell differentiation. Importantly, this translocation is rare but associated with a poor prognosis in AML.
MOLM-13 Tumor Kinetics in the SRG™ Rat
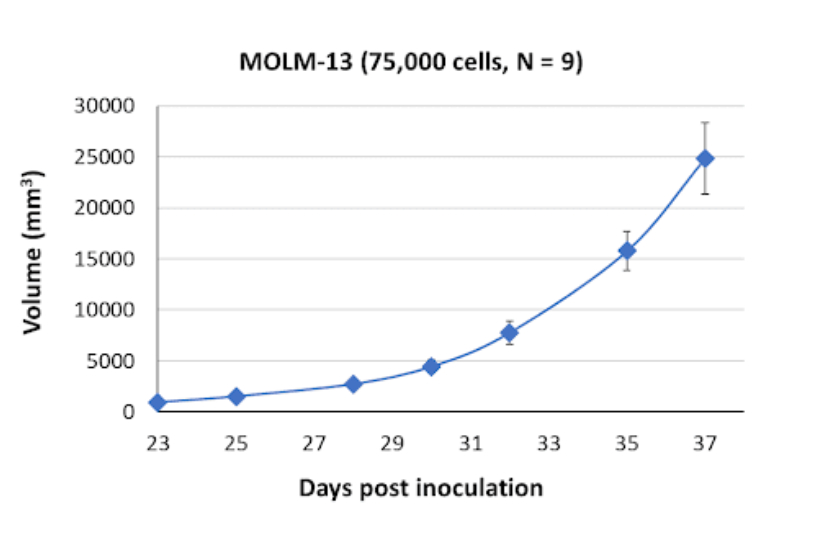
The MOLM-13 cell line holds significant interest in the context of tyrosine kinase inhibitor efficacy studies, such as with midostaurin and quizartinib. These therapeutic agents target specific tyrosine kinases involved in leukemia progression. MOLM-13 cells have been found to be sensitive to these inhibitors, making them a valuable model for investigating their effectiveness and potential mechanisms of action. In xenograft models, where MOLM-13 cells are transplanted into immunodeficient animals, the resulting tumors exhibit distinct characteristics. These tumors are firm and well defined, and over time, they become vascularized due to the formation of blood vessels to support tumor growth. Eventually, the tumors develop areas of necrosis, indicating compromised blood supply and tissue death.
Products & Services
Xenograft Efficacy Studies
Includes collection of blood, tissues & tumor for ADME, PK/PD and analysis.
(Bi)weekly Tumor Sampling
Via fine needle aspiration (FNA). For longitudinal evaluation of drug exposure, histology and gene expression.
OncoRats
Cutting edge models optimized for engraftment.
Get help with your research by scheduling a call with Hera.
References (MLA):
- Fong, Jason T., et al. “Alternative Signaling Pathways as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Overcoming EGFR and C-MET Inhibitor Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.” PLOS ONE, 4 Nov. 2013, journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0078398.
- Harris, Britte, et al. “Variant Translocations (9;11): Identification of the Critical Genetic Rearrangement.” Cancer Genetics Journal, Jan. 1988, www.cancergeneticsjournal.org/article/0165-4608(88)90108-2/pdf.
- “MLLT3 MLLT3 Super Elongation Complex Subunit [Homo Sapiens (Human)] – Gene – NCBI.” National Center for Biotechnology Information, June 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/4300.
